Understanding CT Scan for Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally. Early detection is crucial in improving patient outcomes and increasing survival rates, which is where advanced imaging techniques such as the CT scan for lung cancer play a vital role. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about CT scans, including their significance, how they work, and what patients can expect during the procedure.
What is a CT Scan?
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan is a sophisticated imaging technique that uses X-ray technology combined with computer processing to generate detailed cross-sectional images of the body. These images provide a more comprehensive view than traditional X-ray images, facilitating the detection of abnormalities such as tumors in the lungs.
The Role of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Detection
Early detection of lung cancer significantly enhances treatment options and survival rates. CT scans are particularly effective in identifying small tumors that may not be visible through other methods. Here are some critical aspects of the role of CT scans in lung cancer detection:
- Screening for High-Risk Individuals: CT scans are often recommended for individuals at high risk of developing lung cancer, such as heavy smokers or those with a family history of the disease.
- Diagnosis: When patients present symptoms such as a persistent cough, chest pain, or unexplained weight loss, a CT scan can help confirm a diagnosis of lung cancer.
- Staging: Once lung cancer is diagnosed, CT scans are essential for determining the stage of the cancer, helping doctors understand the extent of the disease and guiding treatment plans.
- Monitoring Treatment: CT scans are used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment, allowing healthcare providers to make timely adjustments to therapy as needed.
How Does a CT Scan Work?
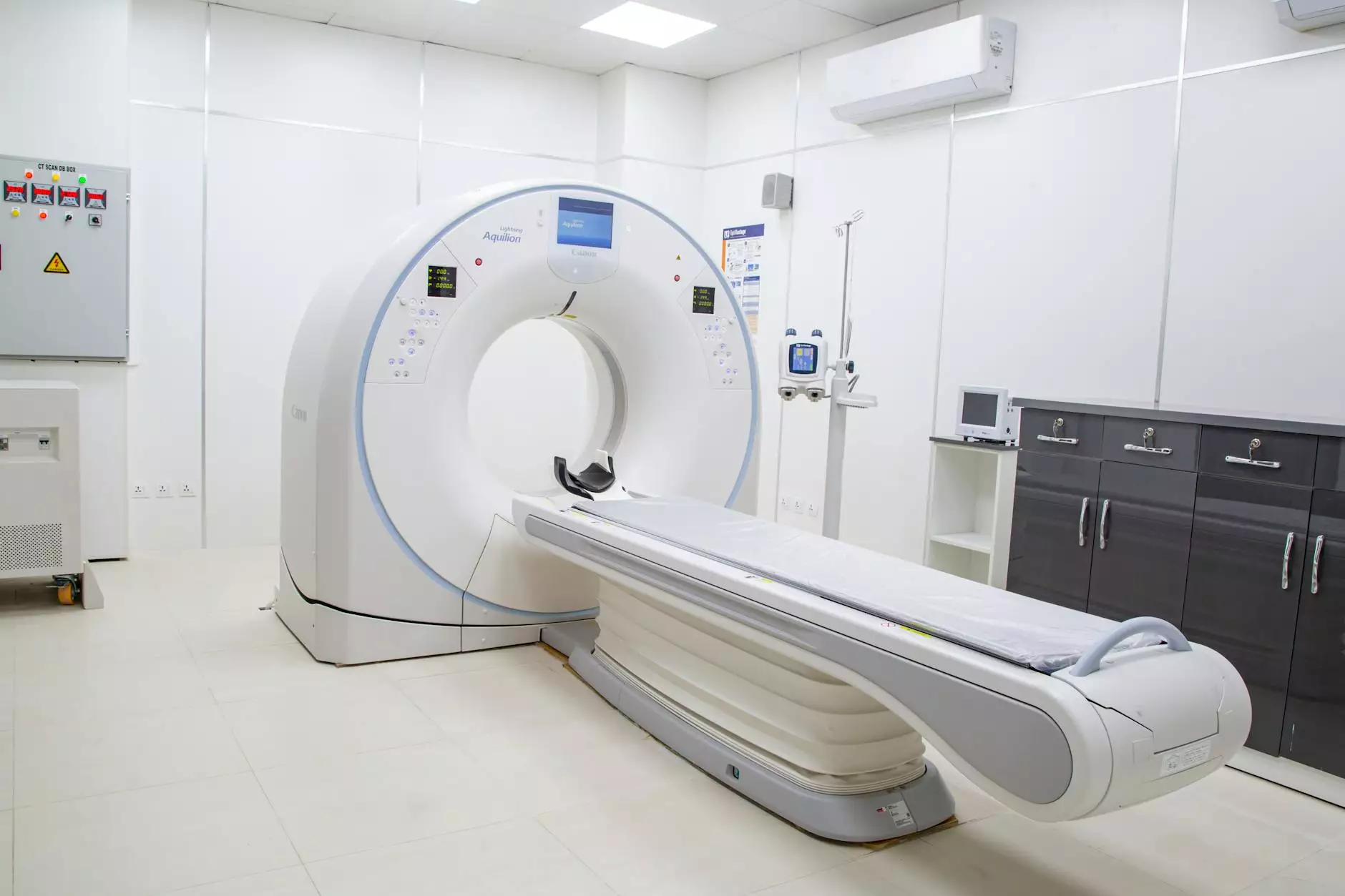
During a CT scan for lung cancer, the patient lies on a table that slides into a large, donut-shaped machine. The machine rotates around the body, taking multiple X-ray images from different angles. A computer then processes these images to create cross-sectional views of the lungs and surrounding tissues. Some important points to consider include:
Preparation for the CT Scan
Prior to undergoing a CT scan, patients may be advised to:
- Avoid eating or drinking: Generally, patients are instructed to refrain from eating or drinking for a few hours before the procedure, especially if a contrast dye will be used.
- Inform the technician: Patients should inform the technician of any allergies, particularly to iodine or contrast materials, as well as any medications they are taking.
The Procedure
The actual procedure typically takes about 30 minutes. Patients will be guided to lie still on the table while the scanner takes images. It is crucial to remain as still as possible to avoid blurring the images. Depending on the specific circumstances, a contrast dye may be injected to enhance the imaging results.
Post-Procedure
After the CT scan is complete, patients can usually resume normal activities immediately. The images will be interpreted by a radiologist, who will report findings to the patient's referring physician.
Benefits of CT Scans for Lung Cancer
Utilizing a CT scan for lung cancer detection comes with several significant benefits:
- Early Detection: The CT scan for lung cancer can detect tumors at earlier stages when they are most treatable.
- Non-Invasive: CT scans are non-invasive, making them a preferable option for many patients compared to other diagnostic methods like biopsies.
- Comprehensive Imaging: CT scans provide detailed images that can reveal not only the presence of tumors but also the size and specific characteristics of the cancer.
- Guidance for Further Treatment: The information obtained from a CT scan can help direct further diagnostic tests or biopsies as needed.
Limitations and Considerations
While CT scans are an invaluable tool in lung cancer detection, they do have limitations. Some factors to consider include:
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans involve exposure to radiation. However, the risk is generally outweighed by the benefits of early detection in high-risk populations.
- False Positives: CT scans can sometimes identify nodules that may not be cancerous, leading to unnecessary anxiety and additional tests.
- Cost: The cost of a CT scan can be a concern, though many insurance plans cover the procedure for eligible patients.
Advancements in CT Scanning Technology
The world of medical imaging is rapidly evolving, with CT technology continuously improving. Recent advancements include:
- Low-Dose CT Scans: New protocols have been developed to reduce radiation exposure while maintaining image quality, especially crucial for lung cancer screening.
- 3D Imaging Techniques: Advances now allow for three-dimensional reconstructions of the chest, aiding in better visualization of tumors and surrounding structures.
- Computer-Aided Detection: Software is being developed to assist radiologists in detecting potential tumors, thereby increasing accuracy.
Conclusion
The CT scan for lung cancer represents a significant advancement in the fight against one of the deadliest diseases. Through early detection, accurate diagnosis, and continuous monitoring, CT scans are crucial in improving outcomes for lung cancer patients. It is vital for individuals, especially those at high risk, to discuss screening options with their healthcare providers to determine the best approach for their health.
For more information about lung cancer screening and treatment options, you can visit HelloPhysio.sg, where we provide resources and care in the realms of Health & Medical, Sports Medicine, and Physical Therapy.









